Charging Up: The Resurgence of Battery Manufacturing in the US
Elizabeth Ruiz
Posted 11/29/2023
Increasing Battery Manufacturing in the US
Recently, the US Department of Energy announced that up to $3.5 billion from the Infrastructure Law will be allocated to support advanced battery manufacturing (and production of battery materials) across the US.
The investment funds will be focused on:
- Building upgraded and expanded facilities to process battery-grade critical minerals, battery precursor materials, components, and cell and pack manufacturing (all critical to clean energy).
- Creating and keeping well-paid union jobs in manufacturing and low- and moderate-income communities.
- Reaching a net-zero emissions economy by 2050.
- Converting half of all new light-duty vehicle sales to electric by 2030.
- Building a domestic supply chain/reducing reliance from foreign entities of concern.
- Supporting the goal of 40% of overall benefits of certain federal investments being used to help underserved and overburdened communities (read more about the Justice40 initiative).
- Boost the US global competitiveness and meet the growing demand for advanced batteries…and more
Smart Manufacturing and AI/Machine Learning in Battery Manufacturing
The gradual change to electric vehicles as well as different regulations are creating a much higher demand within the battery industry to keep up. How can smart manufacturing/machine learning help increase the very complex production of batteries and battery materials while meeting business targets?
Smart Manufacturing
According to SIEMENS Digital Industries Software, smart manufacturing can assist with planning better production lines, lower commissioning time, scaling to giga-level, and minimizing scrap.
SIEMENS also suggests the use of a digital twin to help design and confirm the functionality of the entire plant layout from manufacturing lines to operating processes.
The battery digital twin can be used in identifying the best configuration for manufacturing lines, simulating scenarios that will or may happen in the future, locating any bottlenecks quickly and efficiently, tracking energy consumption towards the goal of more efficient use, and practicing scaling at the same time as protecting intellectual property.
Smart manufacturing also promotes the standardization of battery machines and operations through horizontal and vertical integration – helpful in cutting time for equipment construction and commissioning. Read the ebook from SIEMENS to find out more.
AI/Machine Learning
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) says that machine learning can be used to speed up better understanding of new materials, chemistries, and cell designs while improving battery performance, lifetime, and safety.
Here are some of the ways machine learning helps in battery production and quality:
- Machine learning increases the accuracy of battery life prediction.
- ML quantitative microscopy analysis informs multi-physics models.
- It provides access to high-quality and robust open-source data.
Read this article for a more in-depth description on each bullet point.
ML can also be used alongside the battery digital twin to obtain total visibility and control over operations to achieve operational intelligence.

Safety Tips for Battery Manufacturing Professionals
With the current increase in battery manufacturing, it is important to focus on the safety of the people working in these rapidly changing (and improving) facilities. According to OSHA, lead exposure is the primary health concern for people in battery manufacturing. It is vital to have early warning systems as well as emergency/evacuation procedures established in any battery manufacturing organization.
Safety recommendations from OSHA include:
- Lead safety protocols and procedures – use OSHA’s eTool
- Using proper PPE (eye and face, respiratory, head, foot, hand)
- Respiratory protection
- Hazard communication
Dräger highlights a few dangers related to battery manufacturing in detail:
Fire and Explosions – Lithium-ion batteries produce flammable vapors from solvents and liquid electrolytes which may cause an increased risk of fire/explosion. A thermal runway triggered by damage, short-circuit, or overcharging also poses fire risk.
Hazardous Gases – Solvents and electrolytes from the batteries can be irritating and/or toxic. Other unsafe chemicals such as hydrogen fluoride may be released during certain process steps, recycling, or during a battery fire.
Airborne Particles – Active materials in battery electrodes are processed in powder form and can cause health problems if respiratory protection is not used during filling, transferring, and mixing. If process steps are performed in oxygen-reduced environments, make sure your organization has a complete oxygen monitoring process established.
Conclusion
The surge in battery manufacturing in the US, fueled by a significant investment of up to $3.5 billion from the Infrastructure Law, marks a pivotal step towards achieving a net-zero emissions economy by 2050 and a notable shift towards electric vehicles. The funds are set for upgrading facilities, creating well-paid union jobs, and establishing a robust domestic supply chain.
However, the complexity of battery production requires innovative approaches, and smart manufacturing offers solutions such as efficient production planning, digital twins for optimal plant layouts, and standardization for streamlined operations. The integration of AI and machine learning further enhances battery quality and performance through accurate life predictions and advanced microscopy analysis.
As always, safety is #1. Understanding and planning for potential risks such as lead exposure, fire, hazardous gasses, and airborne particles in battery manufacturing is one of the most important focuses moving toward the future. As the US propels forward in the battery industry, a blend of strategic investment, technological innovation, and stringent safety measures will undoubtedly shape the future of clean energy.

Midweek with Maintenance World
Looking for a midweek break? Keep up with the latest news brought to you by the Maintenance World Crew.
Related Articles

Cardinal Manufacturing, Helping to Bridge the Manufacturing Skills Gap
South Carolina Ranked as the #1 State for Manufacturing

The Decade of American Reshoring
Lost Radioactive Capsule Proves Preventive Maintenance is as Important as Ever

HBD Condition Monitoring Devices at the center of Ohio Derailment
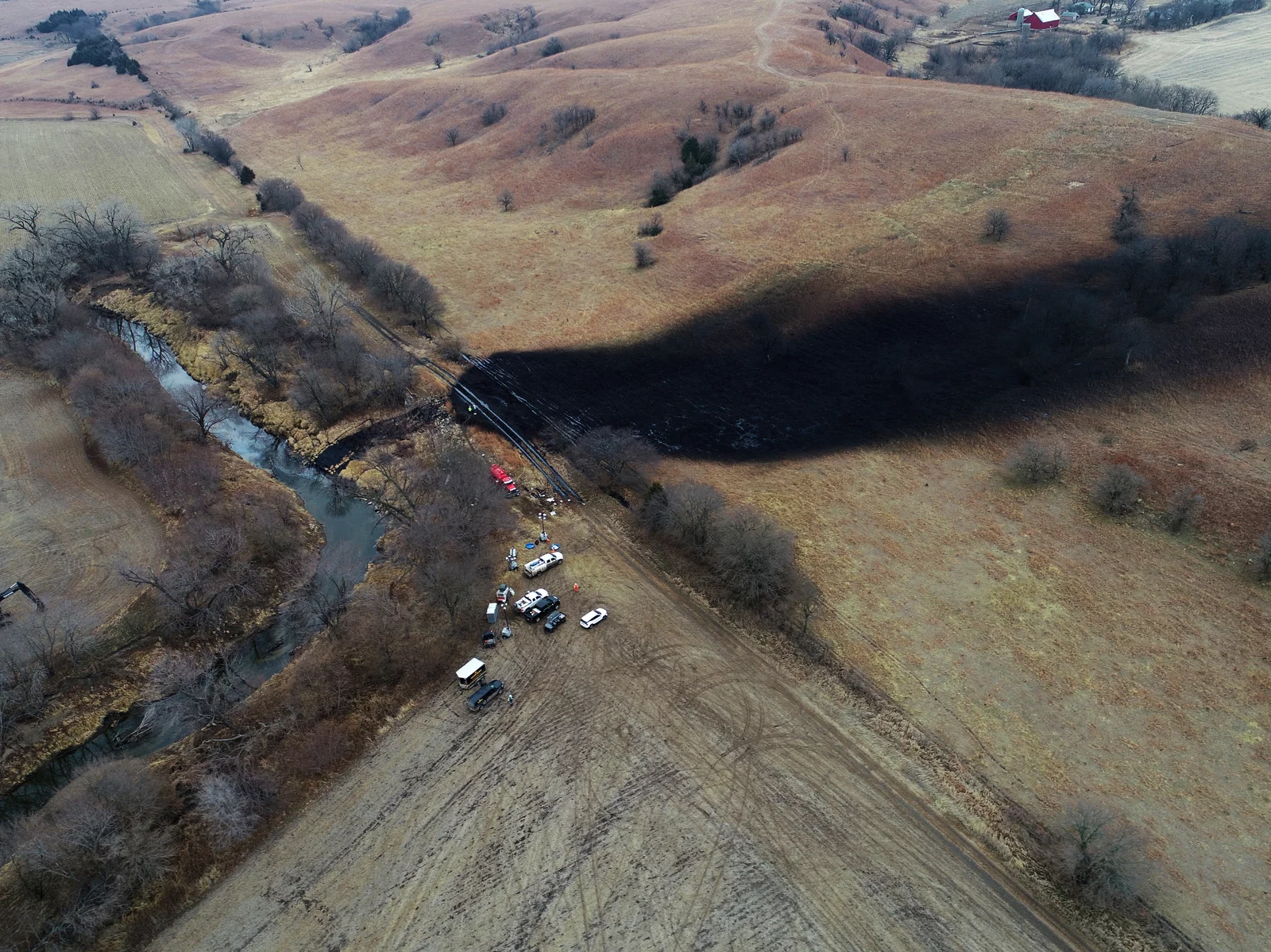

Failure Analysis Uncovers the Cause of the Keystone Oil Spill