Ammonia Safety Precautions: How to Incorporate Predictive Maintenance and the CMMS for Safe Ammonia Use
Elizabeth Ruiz
Posted 11/1/2023
Ammonia is and has been commonly used for refrigeration and flash freezing across many industries, including food and beverage and chemical manufacturing. While it is safe when proper ammonia safety precautions are followed, leaked ammonia can pose serious threats to plant personnel, emergency response workers, and members of the surrounding community due to its toxicity.
What are the benefits of using ammonia in your processes? What are the specific risks that come with it, and how do you best protect your personnel and community from those risks? According to manufacturing.net, using a strong predictive maintenance program along with a comprehensive CMMS can help you mitigate these risks before they become very real dangers.
Use of Ammonia Across Industries

Ammonia use is widespread in industrial refrigeration and flash freezing due to its low cost, reliability, efficiency, proven usefulness, and safety (if procedures are followed). It also has a low environmental impact.
The New York Department of Health explains that along with food and beverage purposes, ammonia can be used to manufacture plastics, explosives, textiles, pesticides, and dyes, as well as purify water supplies. Ammonia is a very useful and valuable form of cooling for many industries. As we continue to use it on such a large scale, it is important to recognize the potential hazards connected with using ammonia as well as the benefits.
Risks of Industrial Ammonia Use
For use in refrigeration, ammonia is converted into anhydrous ammonia, a colorless, pungent, and toxic gas. This gas is highly flammable and can become explosive if large quantities are released and ignited.
Leaks and releases are another risk, causing dangerous ammonia exposure by inhalation, skin or eye contact, or ingestion. It can cause different health issues such as respiratory distress, eye irritation/burning, and corrosive internal damage.
The higher the concentration of ammonia, the more harmful it is:

An ammonia leak or release can cause serious health risks that should be actively avoided. What can we do to ensure the safety of everyone working in and living close to your plant?
Ammonia Safety Precautions

Sundstrom Safety Anhydrous Ammonia Face Mask Courtesy Acme Tools

Ammonia Safety Precautions Checklist:
- Make sure personnel knows how to correctly handle, store, dispose of, and transport equipment that uses ammonia.
- Always use face protection when handling ammonia.
- Limit the crew’s exposure to ammonia as much as possible.
- Always monitor for ammonia levels and post the information in an easily accessible location of the plant.
- Ensure that your team has proper training on equipment use and chemical handling.
- Use leak/gas detection equipment such as personal multi-gas monitors and area monitors.
- Keep air-purifier and air-supplied respirator devices in stock.
- Keep open-circuit and closed-circuit self-contained breathing (SCBA) apparatuses in stock.
- Check regularly for wear and tear on components such as Schrader caps, thread sealants, neoprene o-rings.
- Inspect for potential leaks, corrosion, or faulty components (use vibration detectors).
- Make sure good ventilation systems are in place.
- Establish containment measures and emergency responses in case of a leak.
Check out this pamphlet from the Minnesota Department of Agriculture for more ammonia safety precautions.
Using Predictive Maintenance with a CMMS for Ammonia Safety

Now that we have covered the basics of ammonia safety, let’s take it a step further. Using the combination of a predictive maintenance program with a CMMS can allow your organization to monitor asset performance and analyze data to detect issues within a centralized platform that manages maintenance activities and automates workflows, improving preventive maintenance.
Here are some of the ways predictive maintenance and CMMS can help to establish a good ammonia risk mitigation strategy:
- Early detection
- Condition-based maintenance
- Task management and compliance
- Asset tracking and maintenance scheduling
- Comprehensive and accurate documentation
- Real-time monitoring and alerts
- Data-driven decision making
List courtesy manufacturing.net
Conclusion
While ammonia offers reliable and cost-effective solutions for industrial refrigeration, its toxicity poses significant risks to personnel and communities if not handled properly.
To address these challenges, the integration of predictive maintenance and a CMMS emerges as a crucial strategy. The combination allows plants to proactively monitor asset performance, detect issues early, and enhance preventive measures through condition-based maintenance and compliance tracking.
By utilizing real-time monitoring, alerts, and data-driven decision-making, the integrated system not only improves operational efficiency but also establishes a robust risk mitigation framework. From asset tracking to comprehensive documentation, these tools contribute to organized and well-managed safety protocols. As industries continue to rely on ammonia for diverse applications, prioritizing safety through advanced maintenance practices becomes imperative, ensuring the secure and sustainable use of this valuable cooling agent.

Midweek with Maintenance World
Looking for a midweek break? Keep up with the latest news brought to you every Wednesday by the Maintenance World Crew.
Related Articles

Cardinal Manufacturing, Helping to Bridge the Manufacturing Skills Gap
South Carolina Ranked as the #1 State for Manufacturing

The Decade of American Reshoring
Lost Radioactive Capsule Proves Preventive Maintenance is as Important as Ever

HBD Condition Monitoring Devices at the center of Ohio Derailment
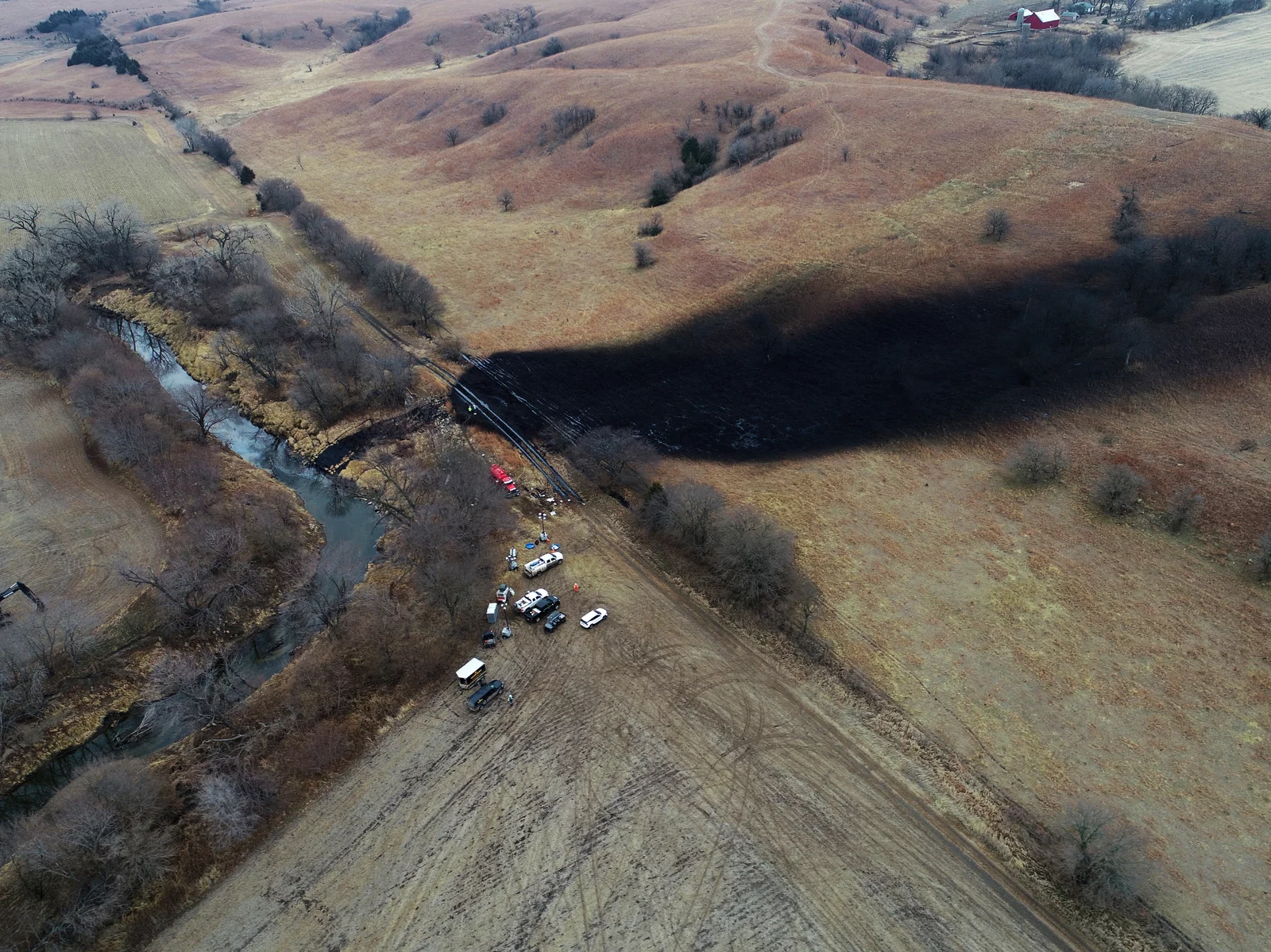

Failure Analysis Uncovers the Cause of the Keystone Oil Spill